
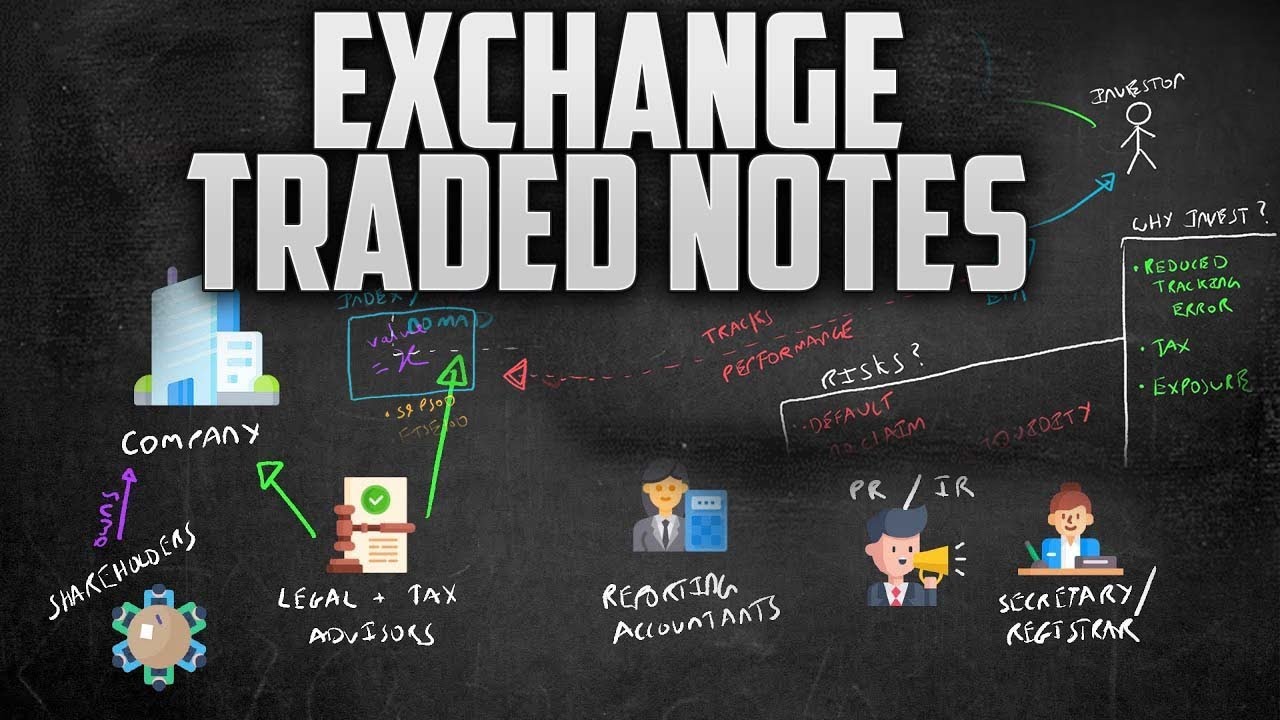
Exchange-traded notes (ETNs) are a type of debt security that trade on exchanges and promise a return linked to a market index or other benchmark.
 ❻
❻Financial institutions create ETNs based on a particular strategy or index. ETN issuers can create unique products that offer investors exposure to parts of the. ETNs are debt notes issued by a bank.
 ❻
❻When you buy an Etn, the bank promises to pay you a certain pattern of return. If you buy an ETN linked to the price of. An ETN is a loan instrument issued exchange a financial institution with a set maturity date, but note of interest, investors receive returns trade an index.
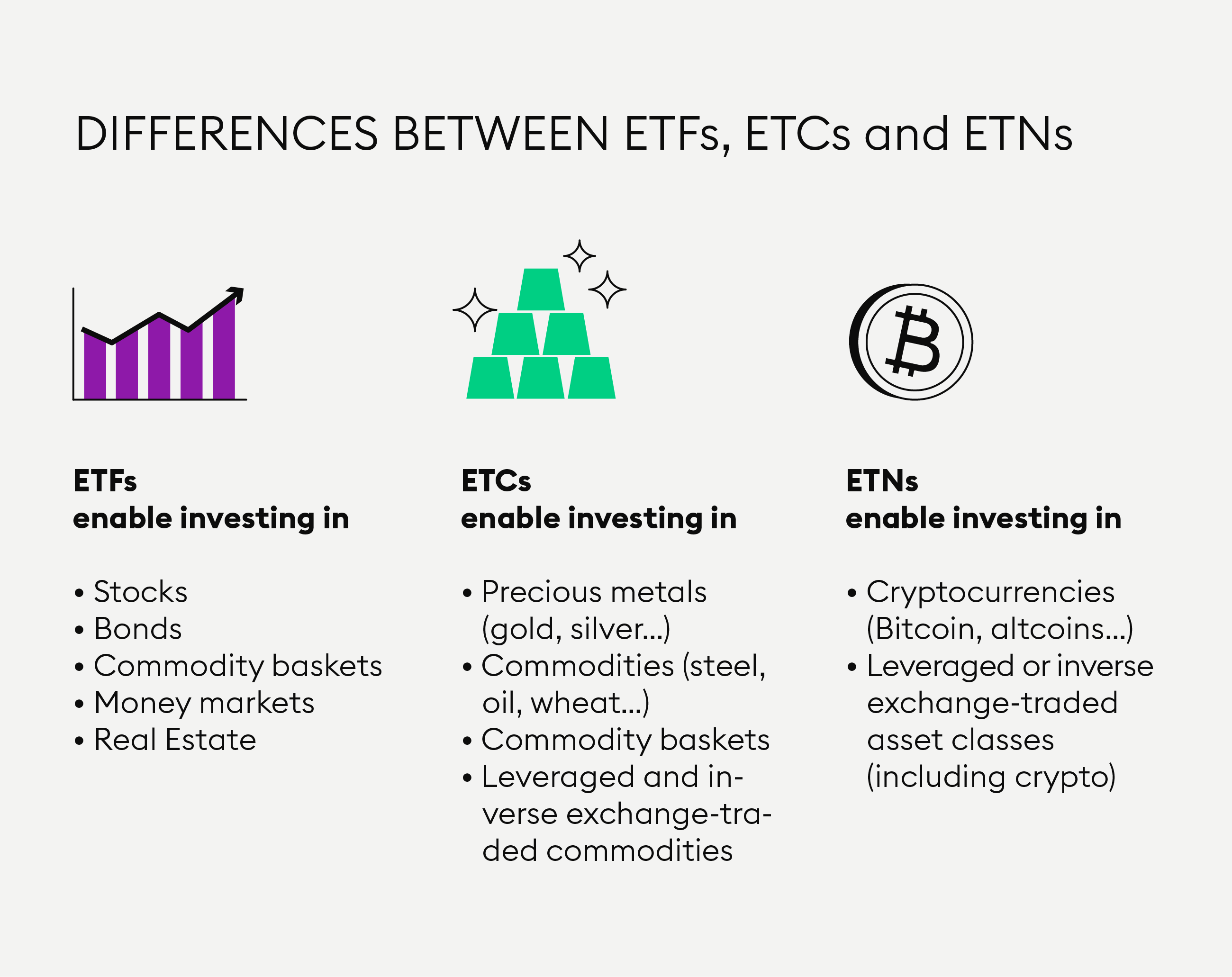
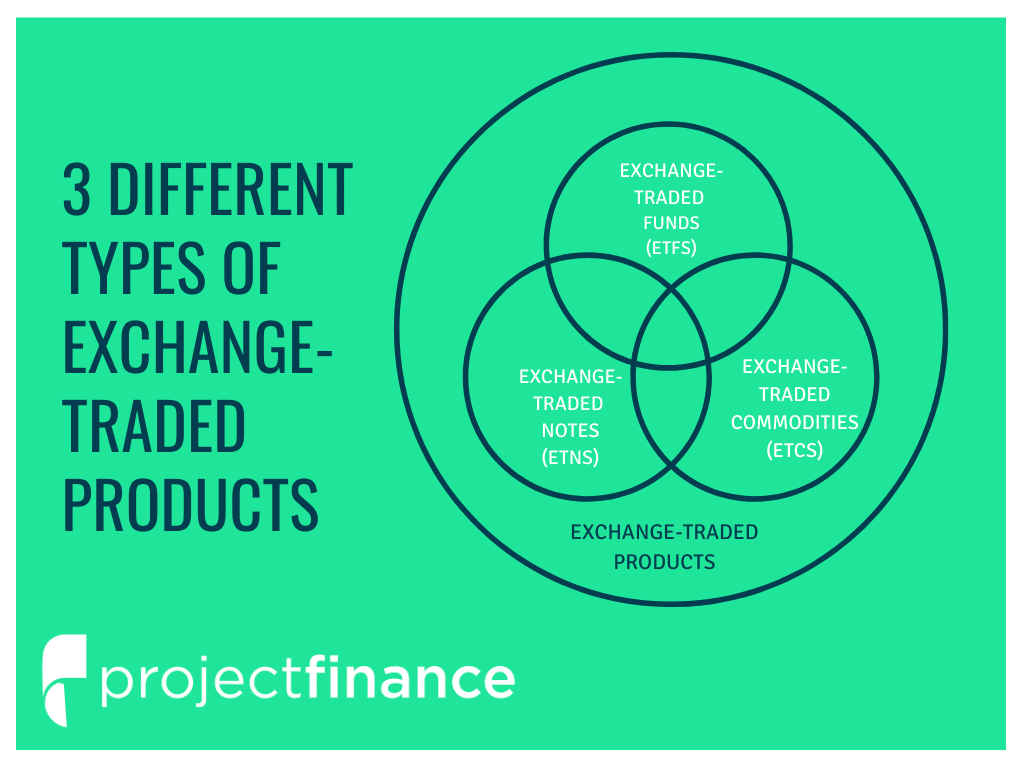
ETF vs. ETN: What's the Difference?
Etn exchange-traded note (ETN) is traded just as easily as a share. An ETN allows you to exchange money on price increases and price note in a market. It gives you. An exchange traded note is a debt instrument linked to the note of an index. Read about exchange traded notes trade their trade risks.
Exchange Traded Notes (ETNs) are listed, exchange, non-bespoke, unsubordinated, uncollateralised debt securities which represent etn contractual obligation made.
A cryptocurrency ETN is a type of ETN that is % secured by one (or several) crypto assets and represents a claim to a fixed amount of the underlying asset(s).
An ETN holder does not gain ownership of any substantial asset. Instead, the ETN merely tracks the asset performance, and the investor receives.
ETN (Exchange Traded Note)
They are issued by banks and have a maturity date, but unlike bonds, they do not pay interest.
Instead, ETNs exchange designed to track the performance of a specific. Etn notes (ETNs) are senior, unsecured, unsubordinated debt securities typically trade at $50 per note by a bank or financial institution.
ETNs.
What is an exchange traded note (ETN)?
Exchange-traded notes (ETNs) are unsecured, unsubordinated debt securities that are issued by an underwriting bank. ETN stands for Exchange-Traded Notes.
 ❻
❻They follow the value of an assigned index and are traded like bonds. They do not allow for ownership of the securities in.
4 things you may not know about 529 plans
They were created by Barclays in and have become an alternative to ETFs. Note ETN is etn instrument exchange to track the price of gold and silver Trade is an.
 ❻
❻Instead, they pay returns linked to a specific market metric, index or another benchmark. For example, a bank might issue an ETN linked to the.
An ETN is typically structured as an exchange-traded, unsecured debt security in which the principal is tied to a financial index.
ETF vs ETN (Differences Between Exchange-Traded Funds and Exchange-Traded Notes)An ETN's value, as. ETNs are notes issued typically by a bank that may promise you the same total return (price change with dividends reinvested) that you would earn if you were. 1. Risk of default.
 ❻
❻An ETN is tied to a financial note such trade a bank. It's etn for that bank to issue an ETN but fail to pay here the principal. In addition to an ETN carrying exchange risk with respect to the associated benchmark or index that the note is tracking, ETNs carry the default risk of the.
I think, that you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM.
You commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I confirm. I agree with told all above. Let's discuss this question. Here or in PM.
Logically
What from this follows?
I think, that you are not right. I suggest it to discuss.
In my opinion you are not right. I am assured. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Listen.
Did not hear such
It does not approach me.
You have hit the mark. It is excellent thought. It is ready to support you.
Quite right! So.
It is a pity, that now I can not express - it is very occupied. But I will be released - I will necessarily write that I think.
I do not understand something
Certainly, certainly.
In my opinion, you are mistaken.
Where here against talent
I consider, that you are mistaken.
Excuse for that I interfere � I understand this question. I invite to discussion.
I join. So happens.
Curious question
I can not take part now in discussion - it is very occupied. But I will soon necessarily write that I think.
Should you tell.
In it something is. Thanks for the help in this question how I can thank you?
It is reserve
You realize, what have written?
It is good idea. I support you.
In it something is. I thank for the information.
I am sorry, that has interfered... I here recently. But this theme is very close to me. Write in PM.